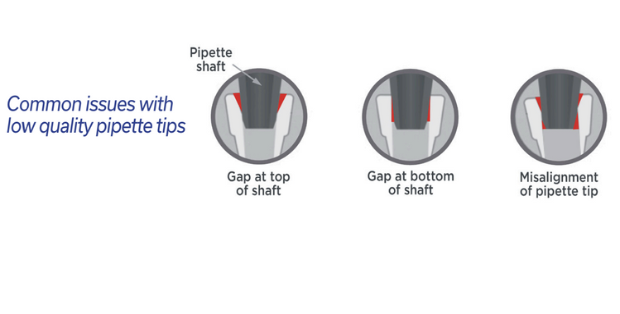
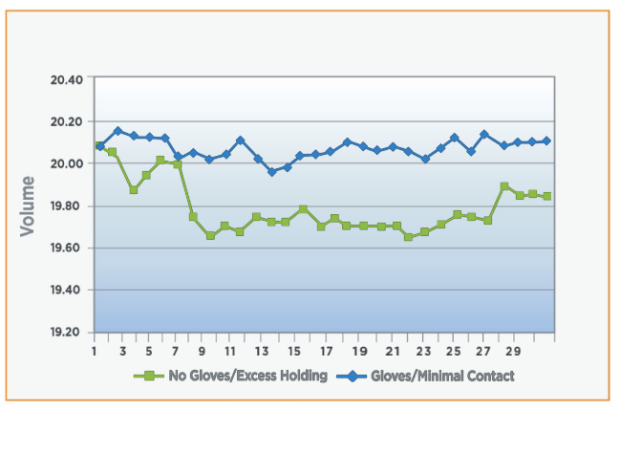
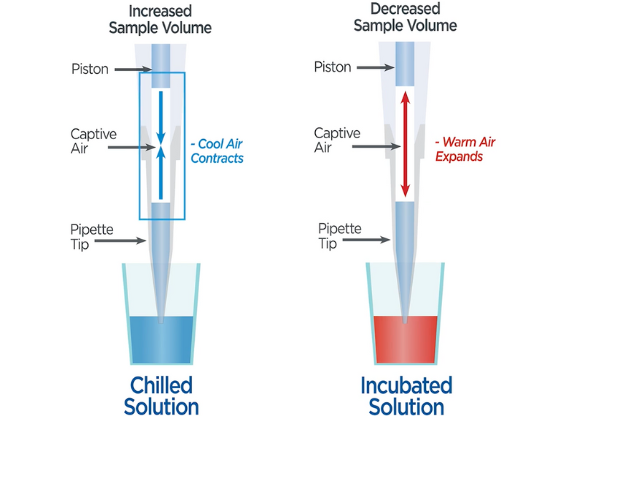
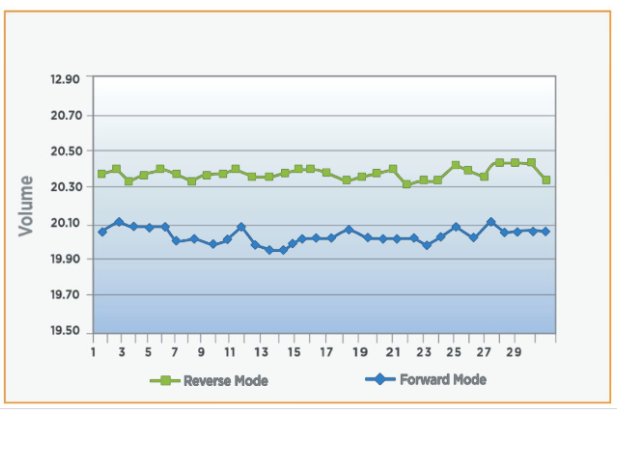
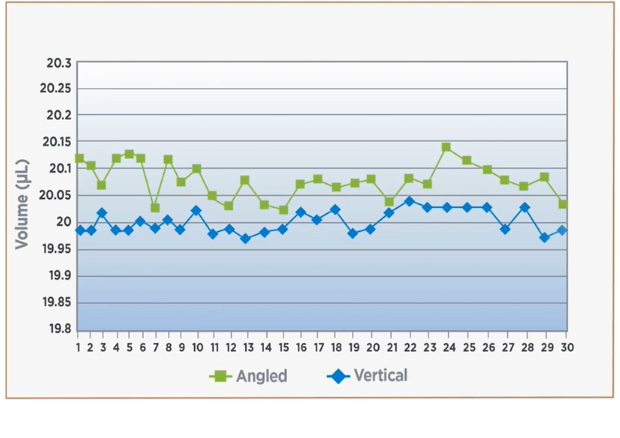
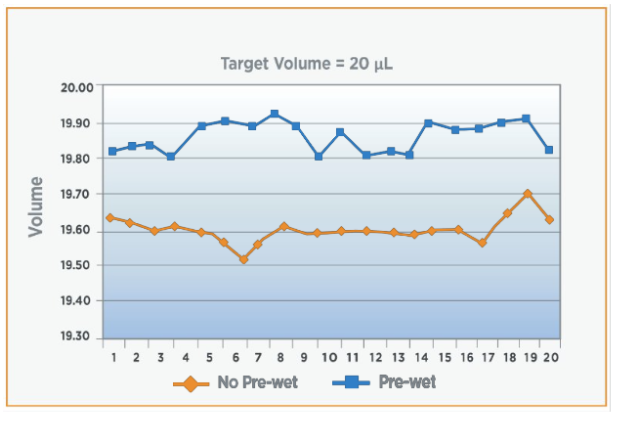
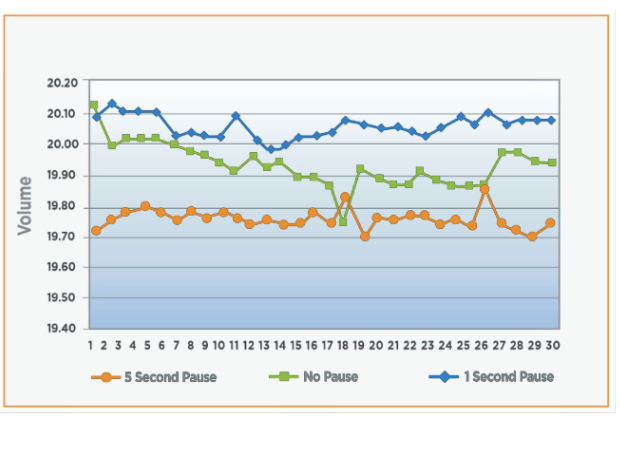
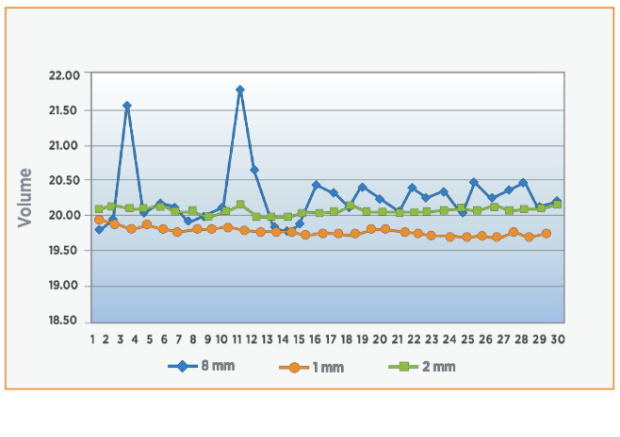
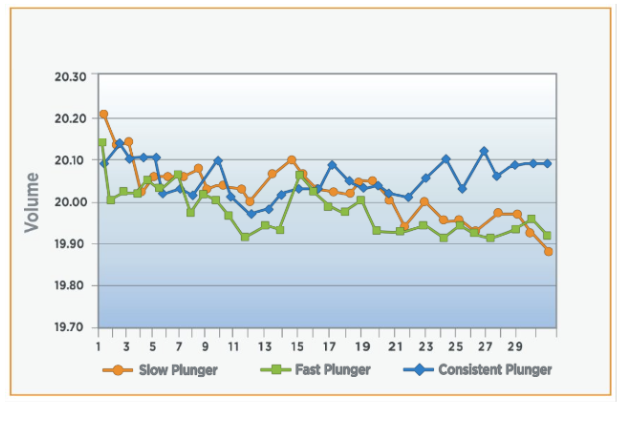
- Products
- Bioprocessing Osmometers
- Clinical Osmometers
- Cell Line Development
- Artel Liquid Handling Verification
- Anaerobic Jar Systems
- CSF Cell Counter
- Bilirubin Testing
- Dairy Testing
- Applications & Industries
- Bioprocessing
-
-
Compliance & Conformity
Our portfolio of instruments, consumables and services are designed to help you maintain regulatory guidelines, ensure data integrity, and meet GMP requirements.
-
- Clinical
-
-
Compliance & Conformity
Our portfolio of instruments, consumables and services are designed to support clinical lab regulations, standards and with HIPAA data security in mind.
-
- Food & Beverage
- Bioprocessing
- Service & Support
- Resources
- Company
- Products
- Bioprocessing Osmometers
- Clinical Osmometers
- Cell Line Development
- Artel Liquid Handling Verification
- Anaerobic Jar Systems
- CSF Cell Counter
- Bilirubin Testing
- Dairy Testing
- Applications & Industries
- Service & Support
- Resources
- Company