Abstract
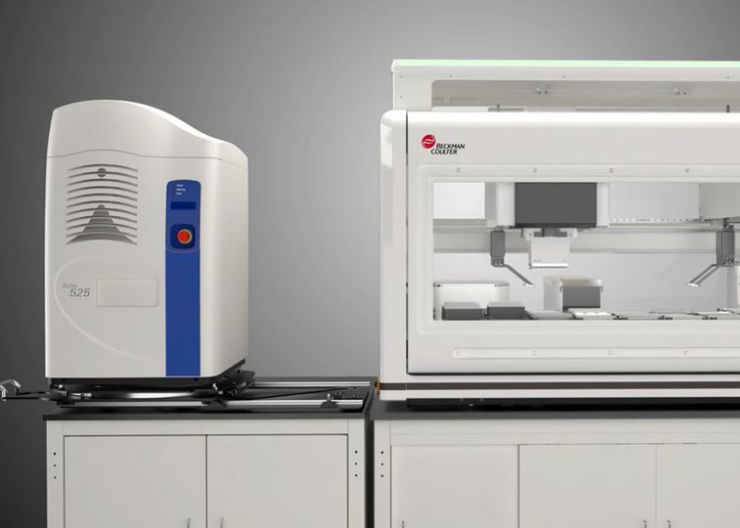
Echo acoustic liquid handlers are automated liquid handlers (ALHs) that use acoustic technology to provide contact-free transfer of liquids in increments of 2.5 nL or 25 nL depending on the model/series. Echo acoustic liquid handlers are compatible with common solvents for biopharmaceutical applications including dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and a variety of aqueous-based solutions. Beckman Coulter Life Sciences currently uses a fluorescence method to evaluate the accuracy and precision of systems, but customers would like an alternative method to validate the performance of the Echo acoustic liquid handlers. An alternative method would minimize downtime and provide immediate performance feedback. Artel by Advanced Instruments provides a complete system, the Multichannel Verification System (Artel MVS), that can be used for liquid handler evaluation. The Artel MVS supports compliance to ISO 23783-2: Measurement procedures for the determination of volumetric performance. This study was designed to evaluate whether the Artel MVS and Beckman Coulter Life Sciences fluorescence test methods provide equivalent volume verification results at 25 nL and 250 nL on Echo acoustic liquid handler-525 and Echo acoustic liquid handler-655 for select aqueous and DMSO solutions.
Introduction
Echo acoustic liquid handlers use acoustic technology to dispense solutions commonly used in the biopharmaceutical industry, including aqueous-based solutions and DMSO solutions with varying hydration levels. The dispensing process from acoustic source plates and/or vials is contactless, with volumes as low as 2.5 nL or 25 nL depending on the model/series. The low nanoliter incremental volume delivery approach allows the direct preparation of assay plates at varying concentrations of reagent, by simply adjusting the number of increments dispensed per well. The time requirement per dispense causes a practical limitation of this approach for larger volumes, but volumes up to 1,000 nL are commonplace. The contactless dispense minimizes the potential for contamination of stock solutions, an important consideration for compound management libraries, and as such the pharmaceutical industry is a key customer. Furthermore, with miniaturization of assays on the rise, Echo acoustic liquid handlers are being used in a variety of laboratories and industries.
Evaluating the performance of ALHs is important to the quality of data collected and conclusions drawn from scientific studies and can be a regulatory requirement. ISO 23783-2: Measurement procedures for the determination of volumetric performance provides an overview of a variety of methods and is a useful reference. When selecting a test method, consideration must be given to accuracy and precision specifications of the ALH under test. The performance specifications for Echo acoustic liquid handlers are 8% CV and 10% Inaccuracy. A good rule of thumb for selecting a test method to evaluate precision of an ALH is to exceed the limits of the method by at least a factor of 1.5. For example, the Echo acoustic liquid handler imprecision of 8% CV, divided by 1.5 would require a test method to have a % CV specification of 5.3%. When selecting a method for volume verification, the true volume is defined as the True Volume = Reported Volume ± Measurement Uncertainty. When the Method Uncertainty uses a coverage factor (k) equal to 2, that corresponds to two-standard deviations or a two-sigma confidence interval. For normally distributed data, this means the True Volume may be expressed as above with a confidence of 95%. An acceptable uncertainty is ½ the inaccuracy specification of the ALH under test. For Echo acoustic liquid handlers this would correspond ± 5% of the test volume. In summary, the test method should have a % CV of less than 5.3% and an inaccuracy of less than 5% to be used to evaluate Echo instruments with the volume delivery specifications noted above.
Please fill out this brief form to download this content.